![]() Hotline:18637200951
Hotline:18637200951

![]() Hotline:18637200951
Hotline:18637200951


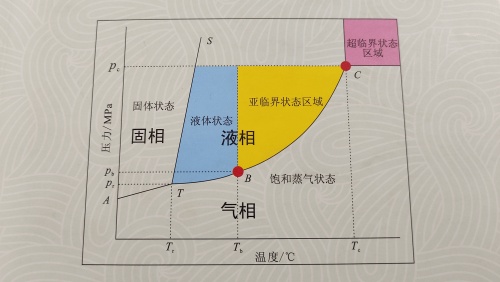
A solvent exists in a liquefied state at a certain pressure in a temperature interval above its boiling point but below its critical point, which we define as the subcritical state of the solvent.
The solvents used for extraction of biological components in this state are subcritical extraction solvents by utilizing their physical properties of similar solubility, and their extraction processes are called subcritical extraction processes.
Suitable for extraction and desolvation solvents at room temperature and lower temperatures, we define as low-temperature subcritical solvents, currently there are five main low-temperature subcritical solvents suitable for industrial production: propane, butane, dimethyl enigma (DME), tetrafluoroethane(R134a), and liquid ammonia.
Summarized in one sentence: Subcritical extraction process is a low-temperature, low-pressure and high-efficiency physical methods.